Declaration of Peace and Cessation of War (DPCW) to be thoroughly discussed in this September
The DPCW is unique, as it aims for a cessation of all wars. By the means of prohibiting weapons and transforming them into daily tools, war and warlike activities cannot be initiated. Therefore, sustainable peace can be achieved by implementing this declaration.
Also, it combines fundamental rights both aiming for peace and peaceful dispute-settlement between states as well as peace within states by promoting freedom and peaceful coexistence of religions and beliefs.
It therefore protects human rights as well as the core rights of states. Most of the DPCW addresses fundamental rights already prescribed by international law. By developing those well-established rules, and adapting them to the present and future problems, the DPCW provides a comprehensive instrument of rules to reach sustainable peace.
As those rules become accepted the more states adhere to them, and as they aim for a global application, all states should agree upon the rules prescribed in the DPCW. (See details on DPCW: peacelaw.org)
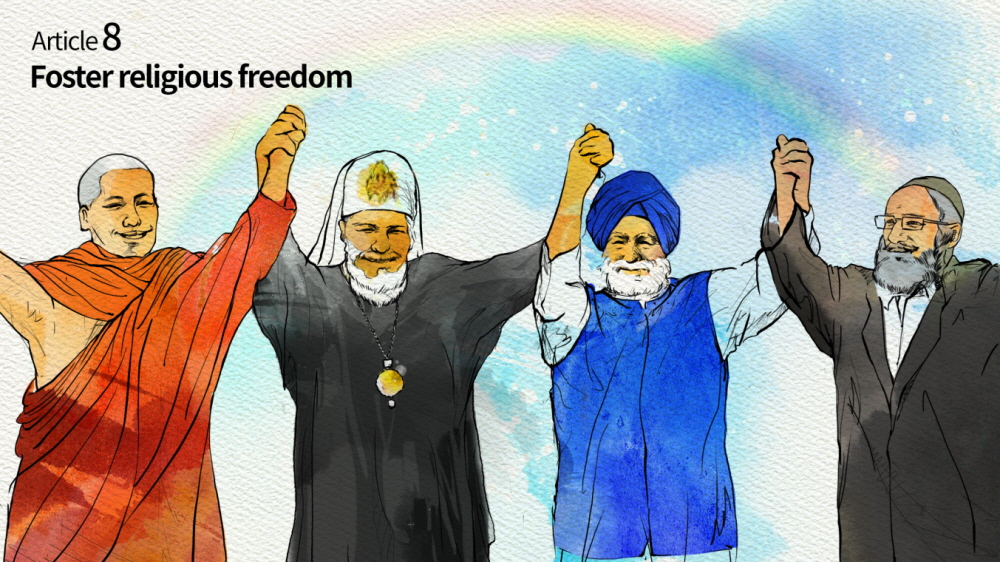

Article 8: Foster Religious Freedom
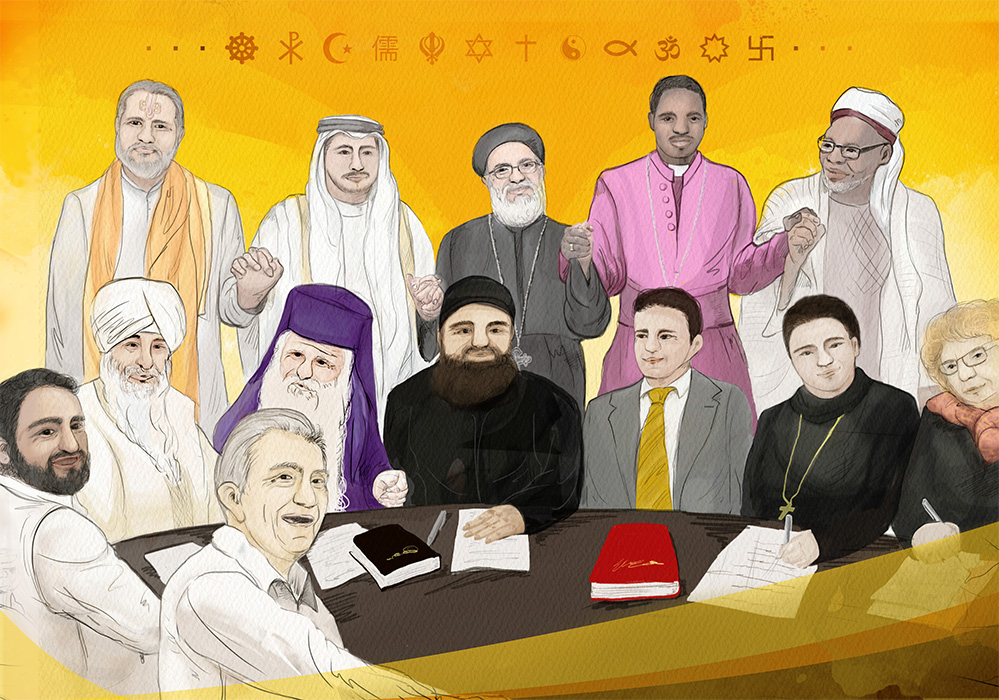
Articles 8, 9 and 10 of the DPCW delineate the means to restore, cultivate, facilitate and enhance the spirit of peace in this globe. In article 8 “Freedom of Religion”, as freedoms are set forth without distinction of religion in the UN Charter, states are responsible for protecting the pursuit of faith, overcoming conflicts caused by misunderstanding and prejudice in religions through promoting interfaith communication, and supporting the active role of religion as a bridge-builder of creation of the world of peace, designated in scriptures as instruction.
The freedom of religion shall be actively protected by states and must not be used as grounds for conflict and/or acts of violence. These contain the rights to adopt, change or renounce a religion or belief, the freedom to manifest one’s religion or belief, the freedom to worship and the protection of places of worship, religious symbols and observation of holidays and days of rest. States must refrain from coercing a religion.

Article 9: Promote Peaceful Coexistence Amongst Religious and Ethnic Groups
In article 9 “Religion, Ethnic Identity and Peace”, states should develop devices that facilitate multilateral consultations and encourage legal measures and social policy for religious and ethnic harmony. Also, legal basis for prosecution and punishment against organizations that promote conflict and violence in the name of religion should be founded.
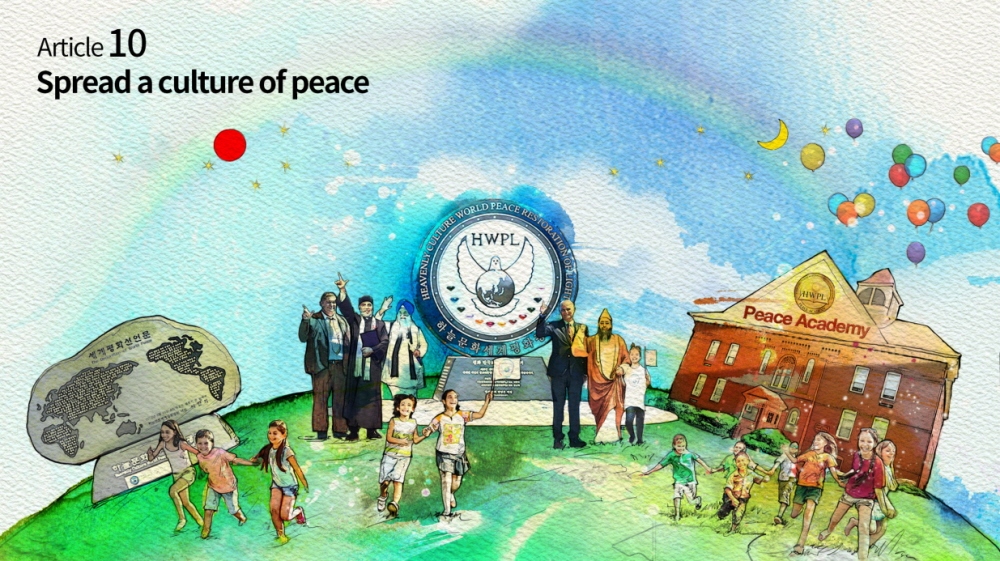

Article 10: Spread A Culture of Peace
In article 10 “Spreading a Culture of Peace”, raising awareness for citizens to develop recognition of peace through education, activities and commemorations is highlighted. Culture facilitates interactions in the community. There is legitimacy of our cooperation for cessation of war and world peace.
When the global community becomes one with the spirit of peace that never fades away in every individual’s heart, the culture of peace will bind us together and facilitate the achievement of the sustainable development goals provided by the United Nations for the common interest that benefits every citizen in our world. The welfare of humanity is dependent on how we can hold our hands together for peace in our times.